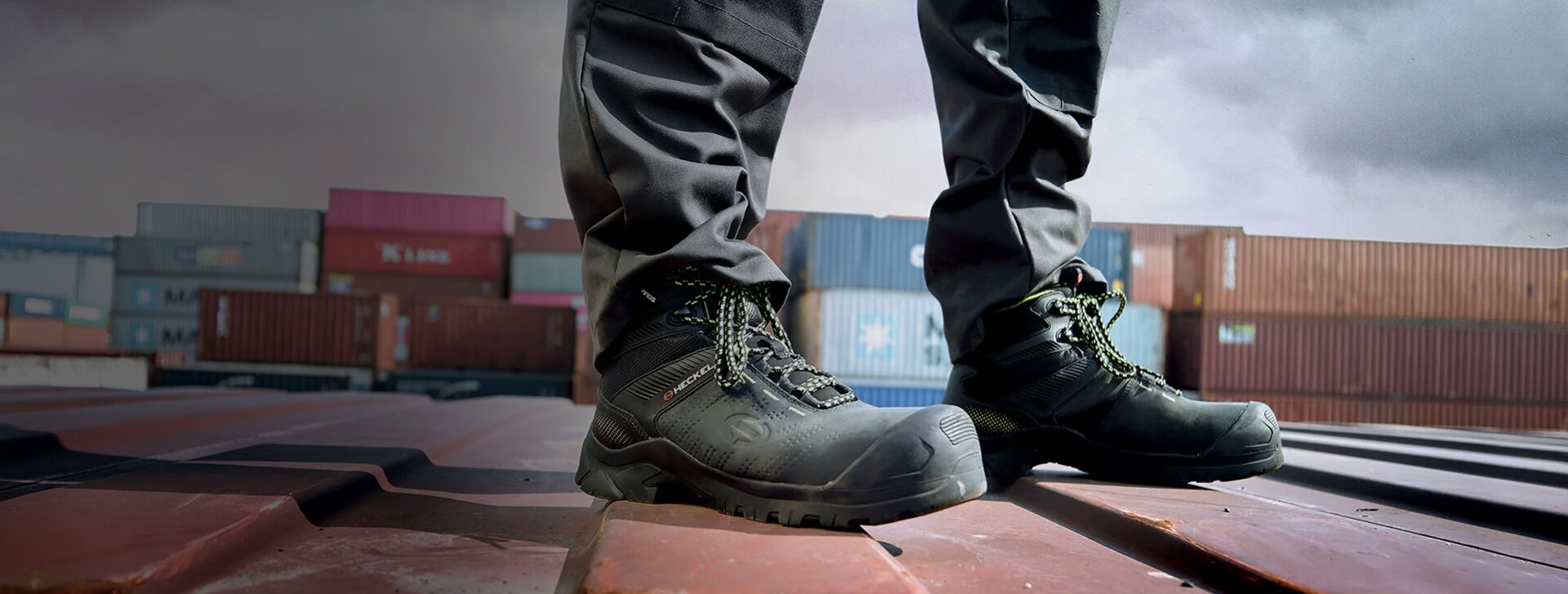

Comprehensive guide to safety footwear standards: protection and compliance
Occupational safety is a top priority in many sectors. Safety footwear conforming to EN 20345 plays an indispensable role in protecting employees against various occupational hazards. These risks include falling objects, impacts and crushes, penetration, corrosive liquids, slipping hazards, water and high temperatures.
This guide aims to detail these standards and characteristics, and to advise employees in choosing the right safety shoes for their working environment.
I. EN 20345 for safety footwear
A. Background to safety standards
Recognised at European level, EN 20345 was first established in 2004 and has been regularly updated since then. Defined by strict criteria for safety footwear, it ensures optimal protection in a range of working environments. This standard was created to harmonise safety standards within the European Union, thus ensuring uniform protection for all employees.
This standard is not to be confused with two other existing standards on the market:
- EN 20346 defines the requirements for protective footwear: these shoes offer a lower degree of protection than EN 20345 with an impact resistance of 100 joules compared with 200 for EN 20345.
- EN 20347 defines the requirements for occupational footwear: these shoes do not need impact protection but do require other types of protection, such as a non-slip or anti-static sole (which reduces or prevents static electricity).
These different standards allow precise selection according to the specific needs of each occupational environment.
B. The fundamental importance of standards for occupational safety
These standards, including EN 20345, are essential in standardising the quality and reliability of personal protective equipment. By setting uniform standards for safety footwear, they play a crucial role in preventing accidents at work, contributing to a safer working environment. Compliance with these standards is a key element in ensuring the protection and safety of employees in various industrial sectors.
- Uniformity and reliability: Standards guarantee consistent quality in protective equipment, providing a solid foundation of trust for users.
- Safety compliance: Employees benefit from products that meet strict standards, allowing them to focus on their tasks with a reduced risk of accident caused by inadequate protection.
- Trust and security: This assurance is crucial to the safety of individuals and makes a positive contribution to the reputation of companies that prioritise a safe working environment for their employees.
C. Criteria and requirements of EN 20345 (SB)
EN 20345 sets out precise requirements to ensure optimum protection from safety footwear. The essential criteria of EN 20345 are as follows:
- The protective toe cap: The standard requires each shoe to be equipped with a protective toe cap that can withstand both impact and compression, defining sufficient residual space inside the shoe. In terms of impacts, the cap is designed to withstand an impact of 200 joules. This is equivalent to an object weighing 20 kg falling from a height of 1 metre. The cap must also be able to withstand significant compression, specifically up to 15 kilonewtons (kN). This is equivalent to the pressure of a mass of about 1.5 tonnes. This specification is fundamental to providing increased safety in situations where feet could be exposed to heavy loads or high pressures, a situation common in sectors such as construction and industrial workshops.
- The other constituent elements of the shoe are also subjected to tests. In particular, the top part of the shoe — the upper — is tested for abrasion resistance, tearing, flexion and even chemical content. The same applies to the insole and the outsole. For the latter, the new version of the 20345:2022 standard now incorporates additional protection with a specific test for slip resistance. Other tests focus on ergonomics and comfort, incorporating these fundamental criteria. The ultimate aim is always to achieve the best possible protection for the user.
- The additional requirements of standard 20345: Depending on the specific needs of each profession, the standard includes many additional requirements such as penetration resistance, heat protection, cold protection, water resistance, electrical conductivity and energy absorption at the heel. All these elements aim to prevent and reduce the risk of injury.
These requirements ensure that safety footwear certified in accordance with EN 20345 offers comprehensive protection that is suitable for a wide range of professional situations.

Toe cap, tested via 200 J drop test and 15 KN pressure test

Resistance, safety and capacity of materials
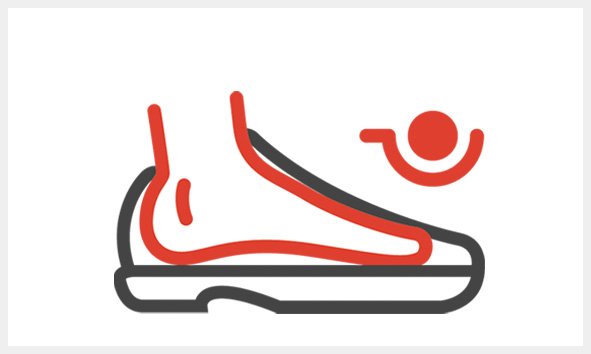
Ergonomics and comfort of the shoe
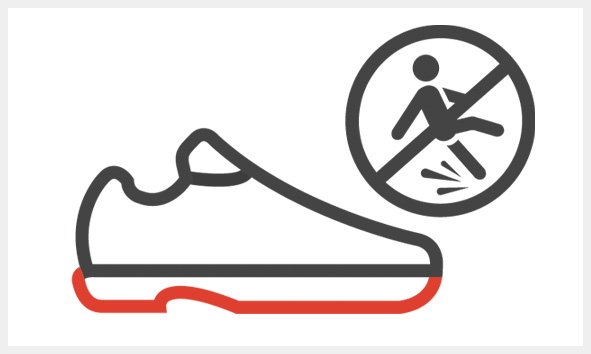
Slip resistance on ceramic tile floors with SLS
II. Detailed classification of footwear according to EN 20345
Footwear conforming to EN 20345 is classified into several categories, each adapted to specific requirements.
Each category is distinguished by unique symbols and marks, indicating the type of protection provided.
This classification makes it easier to choose a safety shoe that is perfectly adapted to the protection needs of each working environment.
A. Protection categories: S1, S2, S3 etc.
Understanding the different categories of safety footwear is essential to choosing the appropriate footwear for different working environments.
Each category offers specific levels of protection, adapted to the various risks encountered in the professional environment.
Below is a detailed overview that describes the requirements and recommended working environments for each category. It will help employees to make an informed choice based on their use.



In addition to the standard categories S1, S2 and S3, EN ISO 20345 also includes the specific categories S4 and S5. They correspond to an advanced range of safety footwear made entirely of rubber and polymer, making them completely waterproof.

EN 20345 was updated in 2022, with two new protection categories added:

B. Additional requirements for safety footwear (EN 20345:2022)
The revision of EN ISO 20345 in 2022 saw the number of additional requirements expand, reflecting advances and changing needs in occupational safety. The following table provides an up-to-date overview of these new requirements, as well as changes to the existing criteria, to keep abreast of the latest developments in safety footwear.

P
Widerstand gegen Durchstich
Metallische Einlage
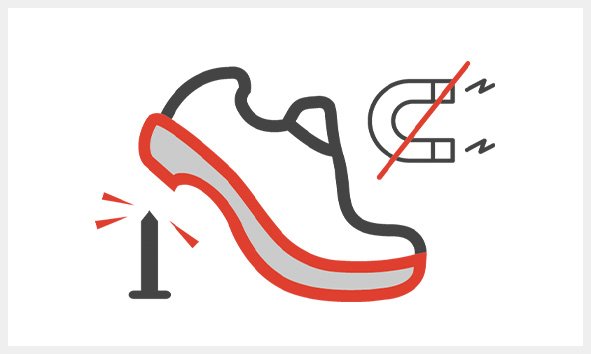
PL
Penetration resistance
Non-metallic insert (test with large point, 4.5 mm)
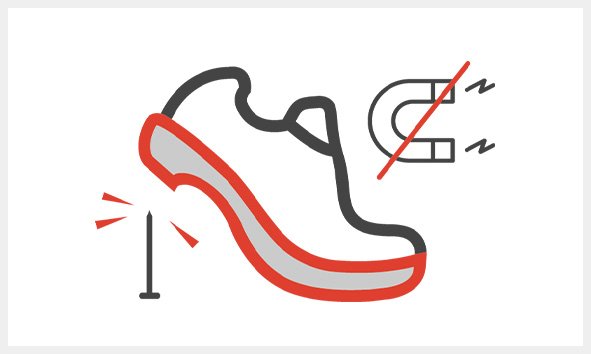
PS
Penetration resistance
Non-metallic insert (test with small point, 3 mm)

WPA
Resistance to water penetration and absorption (upper)

WR
Water resistance (shoe)
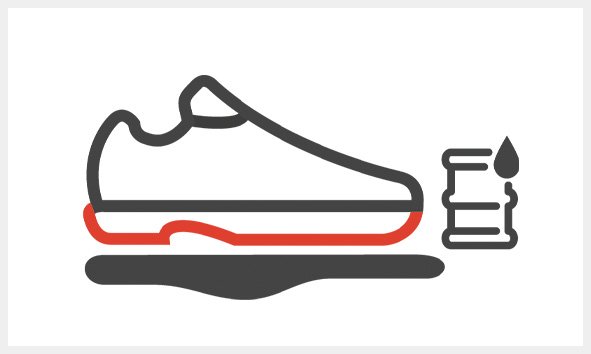
FO
Fuel resistance and oil resistance

HRO
Heat resistance of the outsole

CI
Cold insulation of the sole complex

HI
Heat insulation of the sole complex
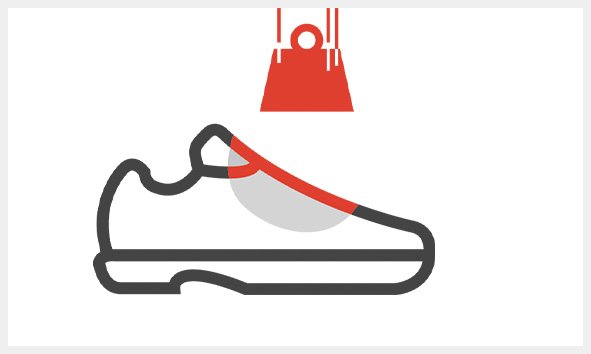
M
Metatarsal protection

AN
Ankle protection
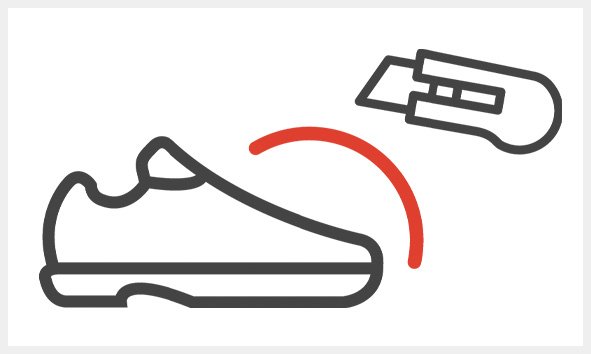
CR
Cut resistance of the upper part of the shoe

C
Conductive footwear
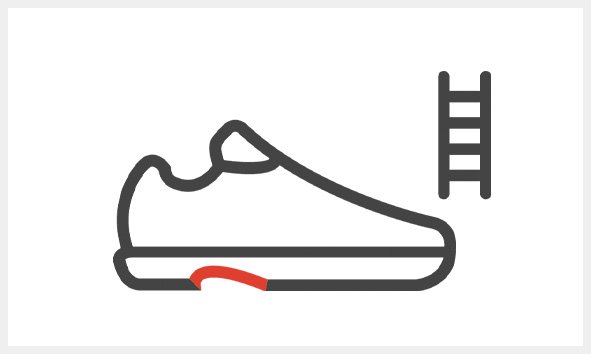
LG
Outsole provide hold on ladders

SC
Abrasion resistance of optional overcaps

SR
Slip resistance on ceramic tile floors with glycerol
III. Adaptation to different working environments
The correct choice of safety footwear is essential to ensure adequate protection in a variety of professional environments. Each working environment presents specific risks, requiring careful selection of footwear according to the appropriate standards and marks.
| Sector | Job types | Risks | Suitable safety shoes | Recommended footwear |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | masons, carpenters, electricians, plumbers, roofers etc. | high risk of falling objects, penetration and slipping | S3 category shoes are often recommended for their penetration resistance, non-slip sole and impact protection | MACCROSSROAD BROWN 3.0 HIGH |
| Manufacturing industry | maintenance technicians, machine operators, forklift drivers etc. | exposure to heavy machinery, compression hazard | S1P or S3 shoes offering protection against penetration are recommended | MS 300 HIGH |
| Outdoor work, wet or muddy environments | gardeners, landscapers, farmers, industrial cleaners, sewage plant employees, shipyard employees | variable weather conditions, exposure to wet and slippery surfaces, extreme temperatures | S3 or S7 are preferred due to their water resistance | MACTRACK 3.0 GTX |
| Logistics and distribution | logistics operators, handling agents, storage and distribution employees, shipping and receiving agents | risks of slipping, falling objects, compression of the foot by heavy equipment, cold or wet environments in warehouses | foot safety in logistics and distribution is paramount due to the various risks associated with handling and moving goods | RUN-R PLANET 300 LOW |
IV. Technological and regulatory monitoring/standards compliance
A. Legislation (France/EU)
In France, the regulation of PPE — including safety footwear — is governed by the Labour Code. Employers are therefore obliged to provide PPE adapted to the occupational risks of their employees and to ensure its effective use. For safety footwear, EN ISO 20345 is often used as a reference to demonstrate compliance with safety requirements.
At EU level, Directive 89/686/EEC has been replaced by Regulation (EU) 2016/425. It establishes the general requirements for the design and manufacture of PPE. In accordance with this regulation, all PPE must bear the CE mark. This indicates its compliance with European standards and guarantees an optimal level of protection.
B. Technologies and innovations at Heckel
These technological advances make Heckel a key player in the safety footwear industry, where innovation goes hand in hand with exceptional safety and comfort:
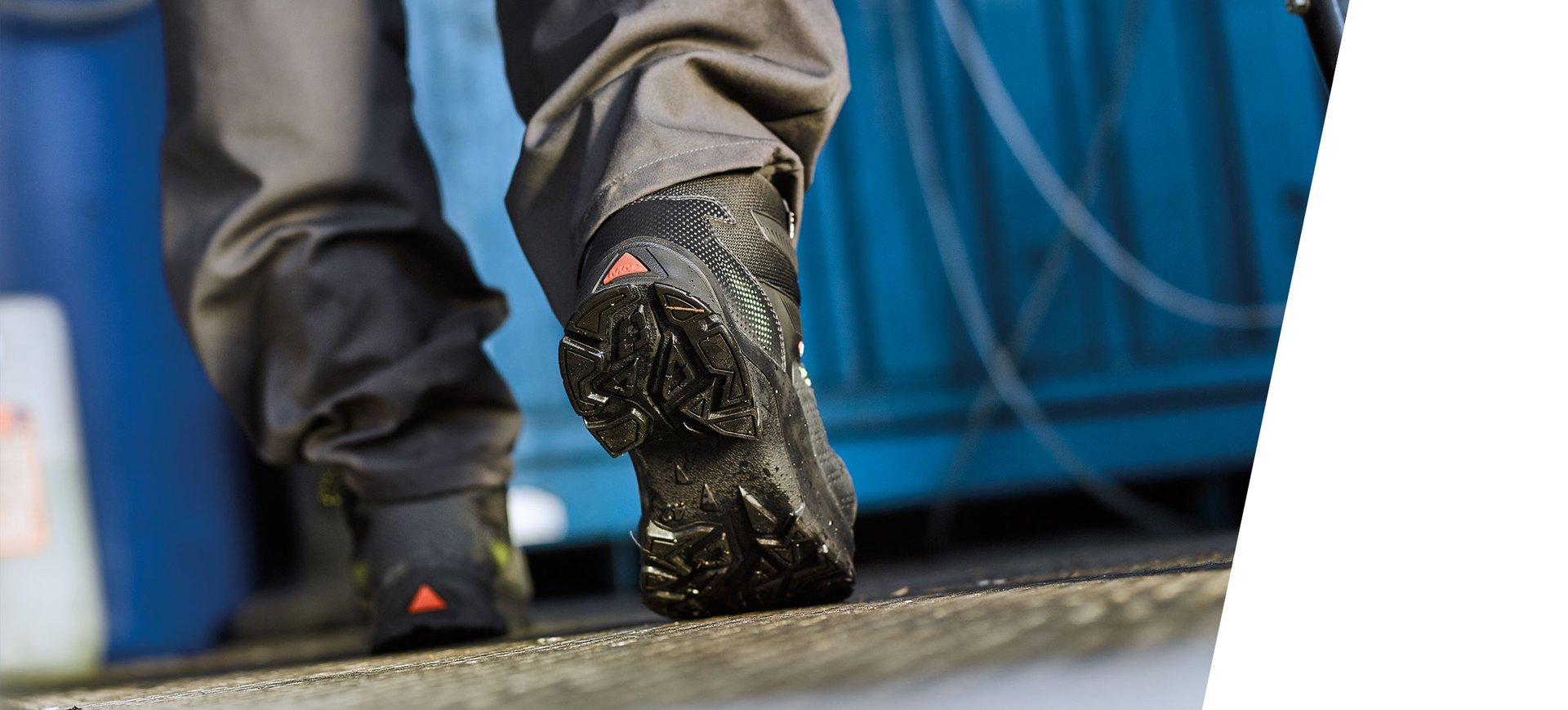

Heckel uses revolutionary materials for increased durability and optimal comfort, with innovations like its own MACSOLE® rubber sole technology. To promote more sustainable development, Heckel also relies on recycled and bio-based materials for the manufacture of its safety shoes, including a large part of its insoles.
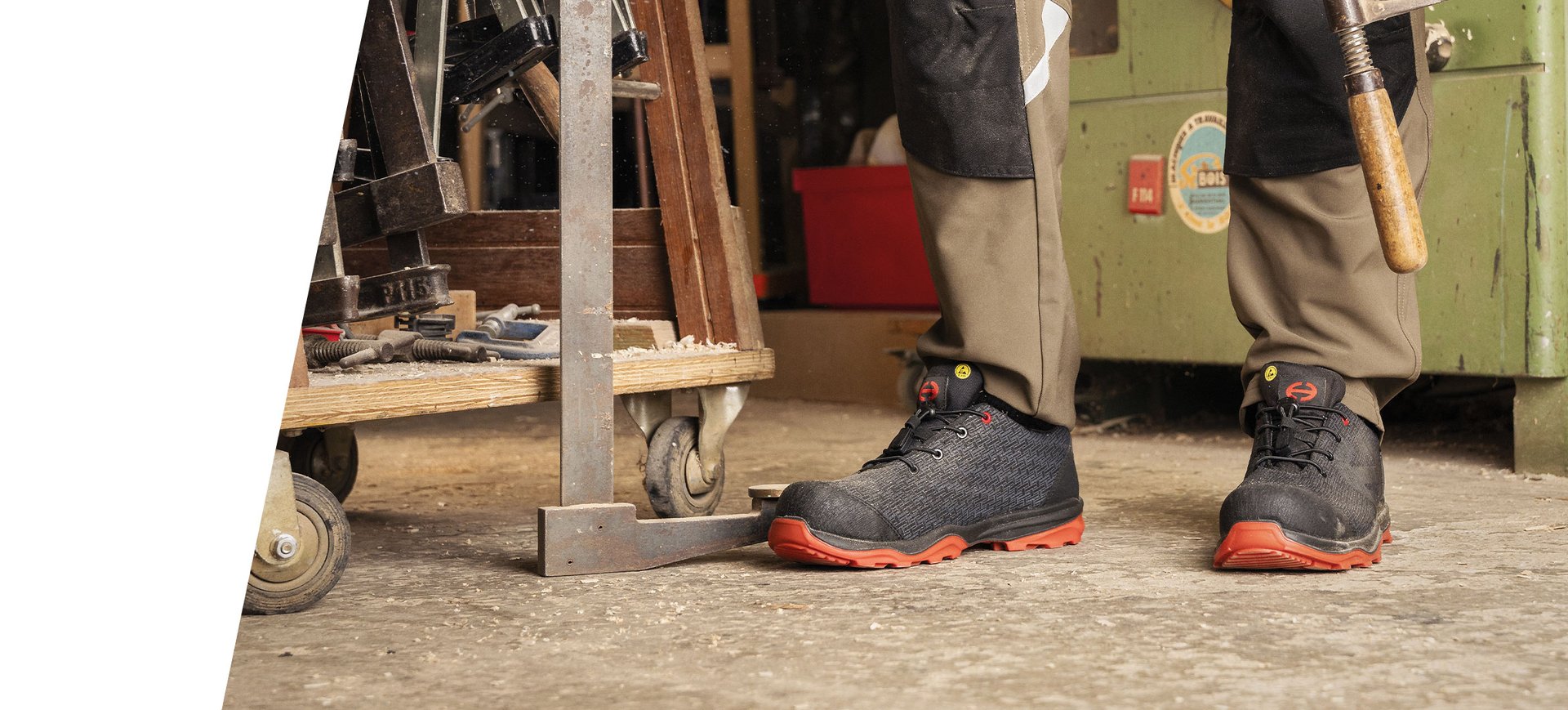

- Advanced protection systems: Heckel shoes are equipped with innovative protection against impact, compression and penetration, ensuring maximum safety for the wearer.
- Non-slip solutions: Complying with non-slip standards, Heckel sole technologies ensure increased stability and safety — even on slippery surfaces.
- Ergonomic comfort: With ergonomic designs and sophisticated cushioning systems, Heckel shoes offer unprecedented support for extended use.
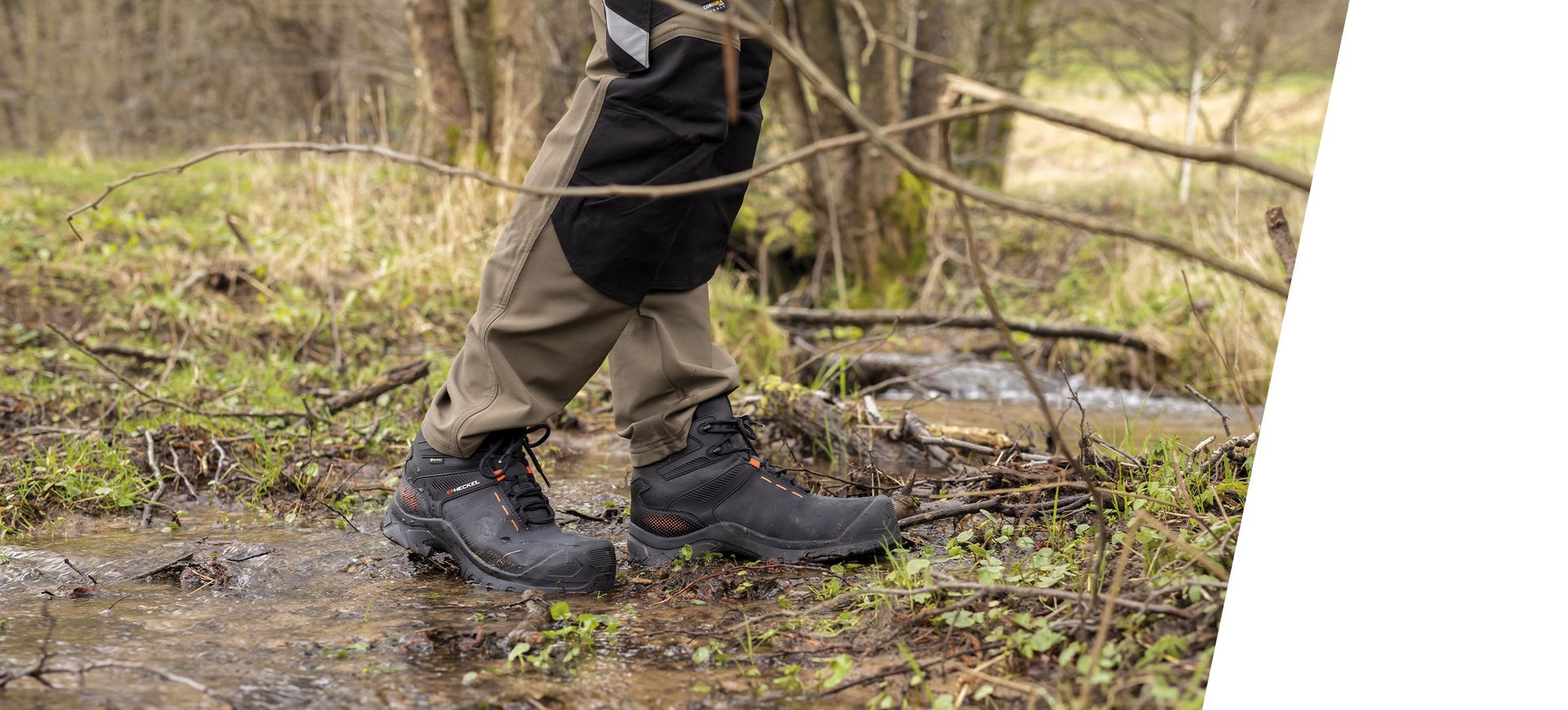

Technologies for waterproofing and insulation: Meeting the needs of extreme environments, Heckel offers shoes with a 100% waterproof Gore-Tex membrane or Gore-Tex insulation that provides thermal insulation down to -30°C.
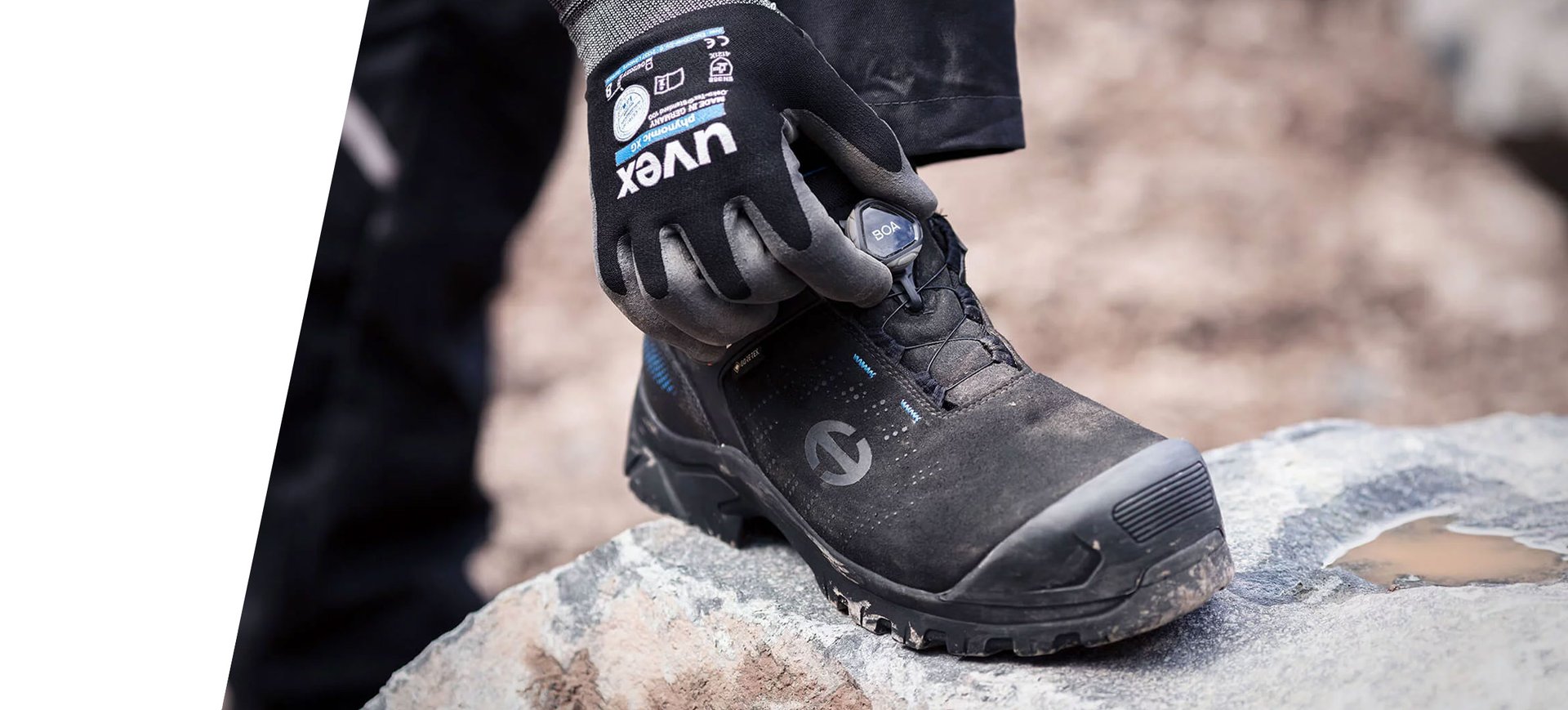

An innovative lacing system for a precise and quick fit, ensuring exceptional comfort and support for the foot. Naturally, we have integrated BOA® closure solutions into some of our safety shoes.
V. FAQs
The main standard for safety footwear is EN ISO 20345. It is recognised at European level. This standard establishes strict requirements to ensure optimum protection in a variety of working environments. It covers aspects such as toe protection, compression resistance and other safety requirements specific to certain professions.
S3 is part of the EN ISO 20345 classifications for safety footwear. S3 standard shoes offer features such as sole penetration resistance, a ribbed sole for improved grip, and water resistance. They are ideal for harsh working environments, such as construction sites and mines.
S5 is another category of EN ISO 20345. S5 shoes are fully waterproof, made of rubber or polymer, and include all the features of the S4 standard (anti-static, energy absorption at the heel) as well as sole penetration resistance and a ribbed sole. They are suitable for extreme conditions, such as in heavy construction industries or intensive agriculture.
ISO 20345 is an international standard that specifies the basic requirements for safety footwear intended to provide protection against various occupational hazards. It includes criteria such as toe protection against impacts and compression, and other specific features depending on the needs of different working environments. This standard ensures uniformity and reliability in the quality of safety footwear across Europe.
To check compliance, look for the CE mark and the category symbol (S1, S3 etc.) on the shoe. These marks indicate that the footwear has been tested and meets the requirements of EN ISO 20345.
EN 20345 relates to safety footwear offering maximum protection, EN 20346 relates to protective footwear with a lower level of protection and EN 20347 refers to occupational footwear without toe protection but able to offer other forms of protection (such as non-slip or anti-static properties).
VI. Glossaries
European standard that specifies the requirements for safety footwear intended to provide protection against various occupational hazards.
Standard for protective footwear offering a lower level of protection than EN 20345, specifically an impact resistance of 100 joules.
Standard for occupational footwear that does not require impact protection but may require other types of protection, such as a non-slip or anti-static sole.
Category of safety footwear that offers basic protection, including toe protection against impacts of 200 joules and compression of 15 kN.
Protection categories defined by EN ISO 20345, each offering specific levels of protection adapted to different working environments.
Categories of waterproof safety footwear made entirely of rubber or polymer, corresponding to the requirements of EN ISO 20345.
New categories added to EN ISO 20345 in 2022, offering advanced water resistance and other protection requirements.
Ability of a shoe to protect the feet from impacts, measured in joules.
Ability of the shoe to withstand compressive forces, measured in kilonewtons (kN).
Ability of the sole of the shoe to resist penetration by sharp objects.
Soles designed to provide better grip and prevent slipping on smooth or wet surfaces.
Former European Directive on personal protective equipment, replaced by Regulation (EU) 2016/425.
European regulation laying down requirements for the design and manufacture of personal protective equipment, including safety footwear.
Mark indicating that the product complies with European standards and guarantees an adequate level of protection.









